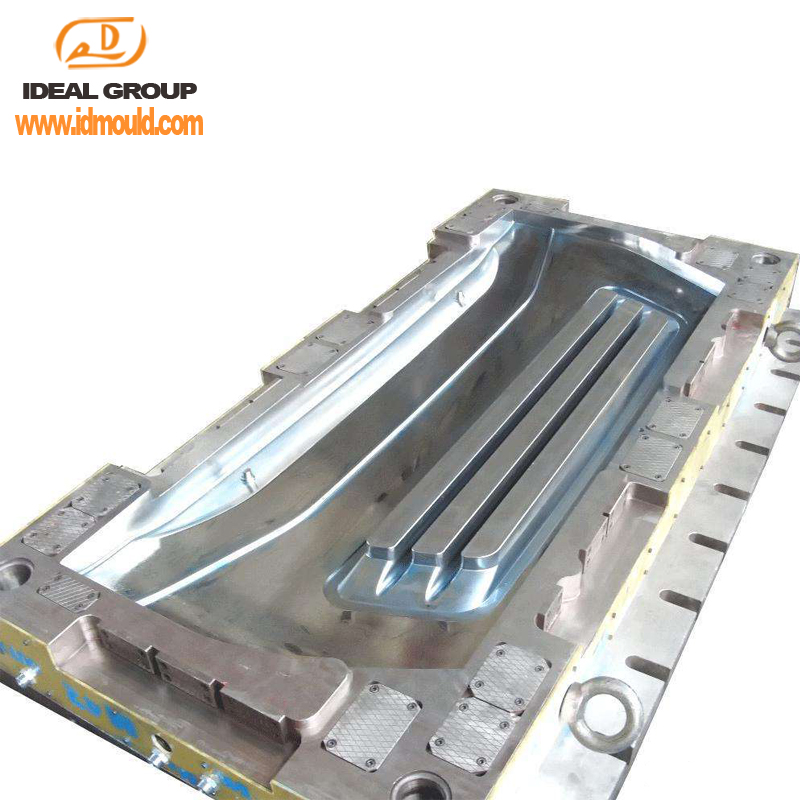
mold maker,mould maker ,plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
Resources
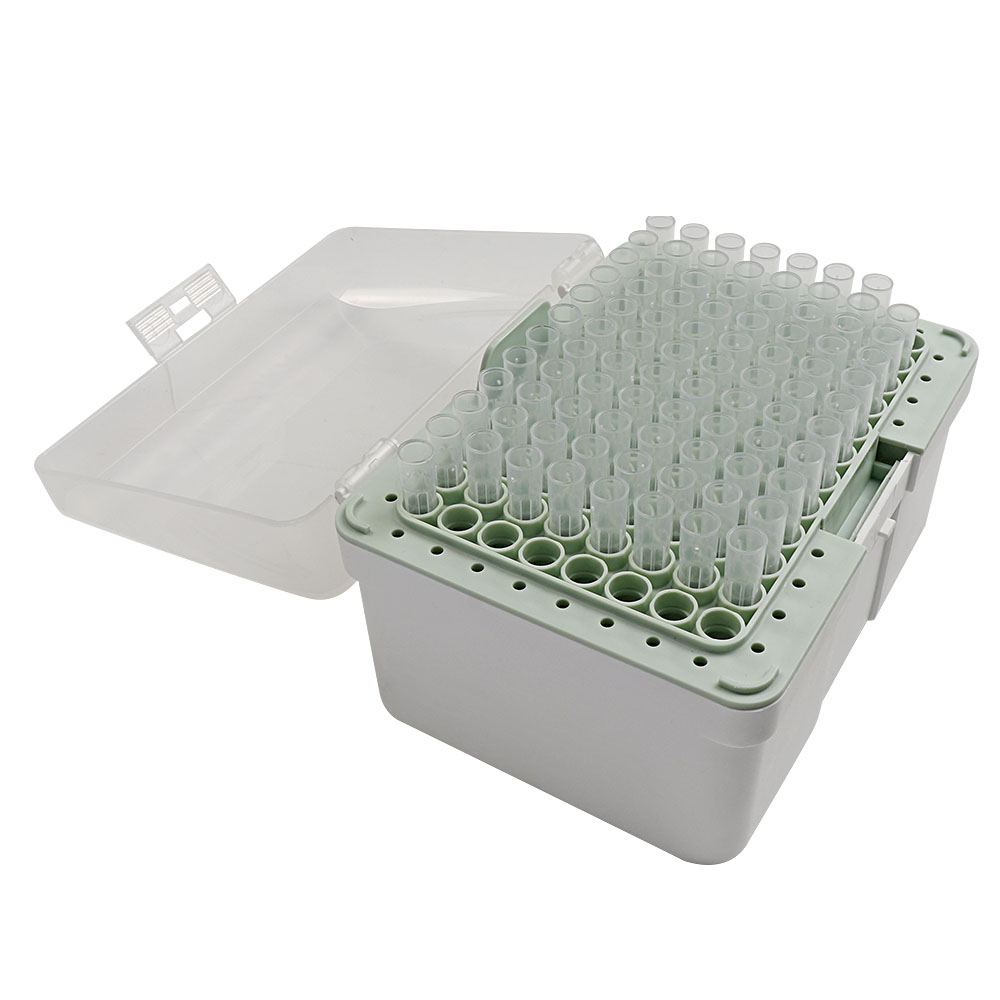
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
plastic mold , plastic injection mold ,mold , injection mold, mould , moulding , plastic injection mould , injection mould
- What do we need to pay attention to the plastic mold machining process and machining procedures?
- What kinds of plastic mold materials?
- What is the process of mold manufacturing?
- What should be paid attention to the polishing of injection molds?
- What is easy to ignore when maintaining and overhauling injection molds?
- What are the 6 systems of plastic molds?
- What are the methods of strengthening the surface of injection molds?
- What are the methods of insulation for injection molds?
- How to solve the problem of injection mold release difficulty?
- How can we increase the brightness of ABS injection molded parts?